 Maintaining homeostasis is necessary for cells to be able to carry out their functions, exist, and replicate.
Maintaining homeostasis is necessary for cells to be able to carry out their functions, exist, and replicate.
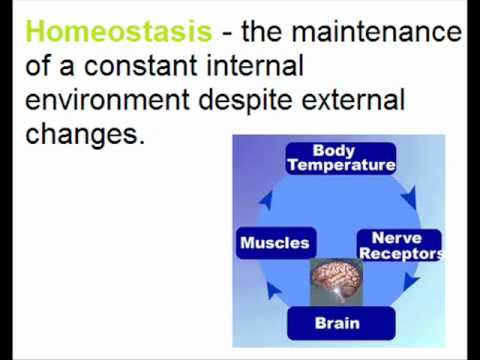
For example, the maintenance of constant species composition and constant numbers of individuals in biocenoses is regarded as homeostasis. Homeostasis can be defined as a property of an organism or system that helps it maintain its parameters within a normal range of values. Biology. Diabetes is a condition where the body cannot regulate its blood glucose levels. Osmoregulation – Also called excretion,... Quiz. Homeostasis (Biology) synonyms, Homeostasis (Biology) pronunciation, Homeostasis (Biology) translation, English dictionary definition of Homeostasis (Biology). The concept of homeostasis is also applicable to biological communities. It is the job of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems throughout the body to maintain homeostasis. ... and that a steady state or homeostasis may be maintained by many systems operating together. Maintaining homeostasis is necessary for cells to be able to carry out their functions, exist, and replicate. This dynamic state of equilibrium is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance , being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). The most important example of homeostasis is life. Scientific American is the essential guide to the most awe-inspiring advances in science and technology, explaining how they change our understanding of the world and shape our lives. Homeostasis is the tendency for the cells in a body, and therefore the body at large, to maintain a stable and consistent internal environment. Diabetes is a condition where the body cannot regulate its blood glucose levels. The stability, or balance, that is attained is called a dynamic equilibrium; that is, as changes occur, the body works to maintain relatively uniform conditions. Homeostasis, in a general sense, refers to stability, balance, or equilibrium. It is dynamic because it is constantly adjusting to the changes that the systems encounter. Homeostasis, in a general sense, refers to stability, balance, or equilibrium. Homeostasis is the regulation of conditions in the body such as temperature, water content and carbon dioxide levels. Homeostasis helps animals maintain stable internal and external environments with the best conditions for it to operate. Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment in organisms e.g same temperature or same pH etc. Biology Definition: Homeostasis is the ability to maintain a constant internal environment in response to environmental changes. Homeostasis is the property of a system within an animal in which a variable, such as the concentration of a substance in solution, is actively regulated to remain very nearly constant. Homeostasis, in a general sense, refers to stability, balance, or equilibrium. homeostasis The principle of self-regulating information feedback by which constant conditions are maintained in a biological system such as the human body. It is a unifying principle of biology. Homeostasis. Related Biology Terms. For any given variable, such as body temperature, there is a particular set point that is the physiological optimum value. Homeostasis is the regulation of conditions in the body such as temperature, water content and carbon dioxide levels. Homeostasis is a regulatory procedure. n. A state of equilibrium, as in an organism or cell, maintained by self-regulating processes: The kidneys maintain homeostasis … In biology, the term homeostasis refers to the ability of the body to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions. Physiologically, it is the body’s attempt to maintain a constant and balanced internal environment, which requires persistent monitoring and adjustments as conditions change. Homeostasis is the property of a system within an animal in which a variable, such as the concentration of a substance in solution, is actively regulated to remain very nearly constant. In biology, it is the keeping of a stable internal environment. Homeostasis is a dynamic equilibrium that is maintained in body tissues and organs. What is Homeostasis? It is a dynamic process that requires constant monitoring of all systems in the body to detect changes, and mechanisms that react to those changes and restore stability. It is in equilibrium because body functions are kept within a normal range, with some fluctuations around a … For example, flushing is … What is … Homeostasis is self-regulation, a basic property of all self-organising systems.
 Maintaining homeostasis is necessary for cells to be able to carry out their functions, exist, and replicate.
Maintaining homeostasis is necessary for cells to be able to carry out their functions, exist, and replicate. Maintaining homeostasis is necessary for cells to be able to carry out their functions, exist, and replicate.
Maintaining homeostasis is necessary for cells to be able to carry out their functions, exist, and replicate.